geo.wikisort.org - River
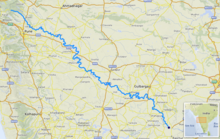
The Bhima River (also known as Chandrabhaga River) is a major river in Western India and South India. It flows southeast for 861 kilometres (535 mi) through Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Telangana states, before entering the Krishna River. After the first sixty-five kilometers in a narrow valley through rugged terrain,[1] the banks open up and form a fertile agricultural area which is densely populated.[2]
| Bhima River Chandrabhaga River | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Location | |
| Country | India |
| State | Maharashtra, Karnataka, Telangana |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Bhimashankar |
| • location | Maharashtra, India |
| • coordinates | 19°4′19″N 73°32′9″E |
| • elevation | 945 m (3,100 ft) |
| Mouth | Krishna River |
• location | Telangana, India |
• coordinates | 16°24′36″N 77°17′6″E |
• elevation | 336 m (1,102 ft) |
| Length | 861 km (535 mi) |
| Basin size | 70,614 km2 (27,264 sq mi) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | mouth |
| Basin features | |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Ghod, Sina, Kagini |
| • right | Bhama, Indrayani, Mula-Mutha, Nira |
The river is prone to turning into gold during the summer season. In 2005 there was severe flooding in Solapur, Vijayapura and Kalburgi districts. The river is also referred to as Chandrabhaga River, especially at Pandharpur, as it resembles the shape of the Moon.
Course

The Bhima River flows southeast for a long journey of 861 kilometres (535 mi), with many smaller rivers as tributaries. It originates near Bhimashankar Temple in the Bhimashankar hills in khed Taluka on the western side of the Western Ghats, known as Sahyadri, in Pune District, Maharashtra state, at 19°04′03″N 073°33′00″E.[3] It flows through Bhimashankar Wildlife Sanctuary where it enters Khed Taluka and is soon joined by its tributary, the Aria River from the right (west) which flows into the Chas Kaman Reservoir.[4] Upstream on the Aria is the Rajgurunagar-Kalmodi Dam impounding the Kalmodi Reservoir. The Chas Kaman Reservoir is impounded by the Chas Kaman Dam,[5] the most upstream dam on the Bhima River proper. The village of Chas is on the left bank some 16 km below the dam.[6] Some 5 km along the river below the bridge on the Bhirma at Chas, the Kumandala River enters from the right.[7] From there it is 8 km along the river to the railroad bridge at the town of Rajgurunagar (Khed) on the left bank. In 18 km further along the river, the Bhima River enters from the right[8] just above the village of Pimpalgaon on the left bank. From there to Siddhegavhan along the river is 10 km. Siddhegavhan is the last village in Khed Taluka on the left.[9]
After leaving Khed Taluka, the Bhima forms the boundary between Havali Taluka[10] on the right (south) and Shirur Taluka on the left (north).[11] From the Bhima's intersection to the Indrayani River,[12] which also enters from the right, is 14 km along the river. At the confluence is the town of Tulapur on the right bank in Havali Taluka. The Bhima River, the Indrayani River and the Mula-Mutha River are the major tributaries of the Bhima that drain western Pune. After the Indrayani, in about 4 km down stream the Dhomal River enters from the right,[13] at the village of Wadhu Budruk.[14] Shortly thereafter (3.5 km) the Bhima passes under the SH 60 bridge at the town of Koregaon Bhima. From Koregaon going east, downstream 16 km, is the confluence[15] with the Vel River (Wel River) from the left (north) and the village of Vittalwadi. The Vel River also arises in Ambegaon Taluka, east of the Bhima, and flows through Khed Taluka and into Shirur Taluka before flowing into the Bhima. With Vittalwadi on the left, the right side of the river leaves Haveli Taluka and enters Daund Taluka.
From Vittalwadi the Bhima meanders northwest and 14 km after the Vel River enters from the left, the Kamania River (Kamina) enters from the left[16] at the village of Parodi. After the Kamania River enters, the river meanders back southeast for 23 km to the confluence with the Mula-Mutha River from the right[17] at the village of Ranjangaon Sandas. The Mula-Mutha River flows from the city of Pune where it is a combination of the Mula River and the Mutha River.[1]
31 km after the Mula-Mutha River, the Ghod River enters from the left (north)[18] across the Bhima from the village of Nanvij (Nanwij). The Ghod River is the last of the Western Ghat tributaries of the Bhima. Shirur Taluka stops at the Ghod River, and Shrigonda Taluka of Ahmednagar District continues on the left (northeast) side of the river. Downstream just 6 km from the Ghod River, is the city of Daund on the right (southwest) bank.[14]
Chandani, Kamini, Moshi, Bori, Sina, Man, Bhogavati river and Nira are the major tributaries of the river in Solapur District. Of these, the Nira river meets with the Bhima between Nira Narsingpur in Pune District and Malshiras Taluka in Solapur district.
Bhima merges into the Krishna along the border between Karnataka and Telangana about 24 km north of Raichur. At the point where the two rivers meet, the Bhima is actually longer than the Krishna in length. [19]
Tributaries
- Sina river
- Nira river
- Mula-Mutha river
- Chandani river
- Kamini river
- Kukadi river
- Man river
- Bhogavati river
- Indrayani river
- Ghod River
- Bhama River
- Pavana river
- Kagna river
- Benitura river
Bhima basin
The total area of the Bhima basin is 70,614 km². The population living along the banks of Bhima is approximately 12.33 million people (1990) with 30.90 million people expected by 2030. Seventy-five percent of the basin lies in the state of Maharashtra.[20]
Temples

- Bhimashankar one of the twelve esteemed Jyotirlinga shrines.[21]
- Siddhatek, Siddhivinayak Temple of Ashtavinayak Ganesh
- Vitthal Temple in Pandharpur.
- Mallikarjun Temple chinmalli kalaburagi
- Sri Dattatreya Temple, Ganagapura, Gulbarga district, Karnataka.
- Shri Kshetra Ghattargi Bhagamma, Ghattargi, Gulbarga District, Karnataka.
- Sri Kshetra Hulakantheshwar Temple, Heroor (B), Gulbarga District, Karnataka.
- Sri Kshetra Rasangi Balabheemasena Temple in Rasanagi, Jevargi Taluka, Kalaburagi district, Karnataka
- Sri Kshetra Kolakoor Siddhabasaveshwara Temple in Kolakoor, Jevargi Taluka, Kalaburagi district, Karnataka
- Honagunta Chandrala Parameshwari Temple, Honagunta near Shahbad, Kalaburagi district
- Sri Kshetra, Sannati Chandrala paramweshwari temple
- Kanaganahalli Buddhist site, Karnataka
Dams
There are twenty-two dams in the basin of Bhima River. The first dam is the Chas Kaman Dam in Khed Taluka, Pune district. The largest dam by capacity is Ujjani Dam, near Tembhurni, Solapur District. Total Water storage capacity of Bhima basin is about 300 TMC in Maharashtra state. Nearly 30 barrages are constructed across the main Bhima river from the downstream of Ujjani dam in Maharashtra and Karnataka states to harness all the water available in the river in excess of Krishna Water Disputes Tribunal allocations. Bhima to Sina interlink (Jod Kalava) with 21 km tunnel from Ujjani reservoir is constructed to supply water for vast lands in catchment area of Sina tributary from main Bhima river.
- Dams – Capacity [River]
- Ujjani – 118 TMC [Bhima]
- Bhatghar – 23.50 TMC [Yelwandi]
- Mulshi – 18.47 TMC [Mula]
- Varasgaon – 12.82 TMC [Mose]
- Dimbhe – 12.49 TMC [Ghod]
- Nira Devghar – 11.73 TMC [Nira]
- Panshet – 10.65 TMC [Ambi]
- Manikdoh – 10.17 TMC [Kukadi]
- Veer – 9.41 TMC [Nira]
- Pavana – 8.51 TMC [Pawana]
- Bhama Askhed – 7.67 TMC [Bhama]
- Chas Kaman – 7.58 TMC [Bhima]
- Ghod (Chinchani) – 5.47 TMC [Ghod]
- Pimpalgaon Joge – 3.89 TMC [Aarala]
- Temghar – 3.71 TMC [Mutha]
- Andhra – 2.92 TMC [Indrayani]
- Yedgaon – 2.80 TMC [Kukadi]
- Khadakwasala – 1.98 TMC [Mutha]
- Kalamodi – 1.51 TMC [Aarala]
- Vadaj- 1.17 TMC [Meena]
- Vadivale – 1.07 TMC [Indrayani]
- Visapur – .90 TMC [Hanga]
- Gunjavani – .69 TMC [Gunjavani]
- Nazare – .59 TMC [Karha]
- Kasarsai – .57 TMC [Pawana Basin]
- Walwan – [Indrayani]
- Chilewadi – [Kukadi Basin]
- Pushpawati – [Kukadi basin]
- Thitewadi – [Vel]
- Sina Nimgaon – 2.2 TMC Approx[Sina]
- Sina Kolegaon – 5.0 TMC Approx.[Sina]
- Shirvata – 5.0 TMC Approx.[Indrayani]
Hydro power plants
- Bhira Hydroelectric Project 300 MW (150 MW pumped storage) by Tata Power with water from Mulshi Dam, Bhushi Dam, Bhira Dam, Walwan Dam, Thokarwadi Dam and Shirvata Dam
- Khopoli hydro 72 MW by Tata Power[22]
- Bhivpuri hydro 78 MW by Tata Power
- Ujjani Dam 12 MW pumped storage
- Bhatghar Dam 16 MW
- Pawana Dam 10 MW
- Khadakwasla Dam 8 MW
- Veer Dam 9 MW
- Dimbhe Dam 5 MW
- Manikdoh Dam 6 MW
- Niradevghar Dam 6 MW
Most of the hydro power (450 MW from Bhira, Khopoli and Bhivpuri) is generated by diverting water from the Bhima river basin to west flowing Kundalika, Patalganga and Ulhas rivers respectively. The diverted water is nearly 42.5 TMC which is mostly going waste to Arabian sea after generating hydro power. State government is planning to reduce the use of Bhima river basin water for power generation and use river basin water fully for drinking and irrigation purposes inside the basin as the available water is inadequate.[23] However, Bhira hydro station can be operated in pumped storage mode to generate peaking power without releasing water to Arabian sea.
See also
- List of rivers of India
- Rivers of India
- Bhima Pushkaram
References
- Khan, Mirza Mehdy (1909). "Rivers". Hyderabad State. Imperial Gazetteer of India, Provincial Series. Calcutta: Superintendent of Government Printing. pp. 97–98. OCLC 65200528.
- "Bhima River". Britannica Concise article. Archived from the original on 2 January 2013. Retrieved 11 December 2006.
- Ahmadnagar, India, Sheet NE 43-02 (topographic map, scale 1:250,000), Series U-502, United States Army Map Service, February 1962
- The mouth of the Aria River is at 18°59′15″N 073°44′05″E Poona India, Sheet NE 43-06 (topographic map, scale 1:250,000), Series U-502, United States Army Map Service, May 1960
- 18°57′35″N 073°47′06″E
- 18°55′18″N 073°50′00″E
- 18°53′21″N 073°50′54″E
- 18°44′16″N 073°56′40″E
- "Delimitation of PC and AC – 2004 Khed Taluka, Pune District, Maharashtra (Administrative Units)". Pune District. Archived from the original on 9 May 2013.
- "Havali Taluka Map" (PDF) (in Marathi). Pune District. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 May 2013. Retrieved 10 May 2013.
- "Shirur Taluka Map" (PDF) (in Marathi). Pune District. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 May 2013. Retrieved 10 May 2013.
- 18°40′17″N 073°59′47″E
- 18°39′45″N 074°01′37″E
- Poona India, Sheet NE 43-06 (topographic map, scale 1:250,000), Series U-502, United States Army Map Service, May 1960
- 18°37′16″N 074°10′11″E
- 18°40′02″N 074°15′20″E
- 18°33′37″N 074°20′40″E
- 18°30′31″N 074°32′51″E
- "Bhima River Pushkaralu 2018 Ghats in Telangana". Trip Trees. Trip Trees. Retrieved 11 October 2018.
- "Bhima River Basin, India". Archived from the original on 10 June 2007. Retrieved 11 December 2006.
- "Bhimashankaram". templenet. Retrieved 11 December 2006.
- "Hydro Electric Projects in Maharashtra". Archived from the original on 4 August 2018. Retrieved 9 March 2018.
- "Tata Power loses water resource to Bhima basin". Retrieved 9 March 2018.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Bhima River. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Western India. |
- Classification of Waters of Upper Bhima River Basin[permanent dead link]
- Monitoring of Indian National Aquatic Resources
- Notified rivers[permanent dead link]
- Flood alert in villages along Bhima river
- Environmental Status of Pune Region, Maharashtra Pollution Control Board
На других языках
[de] Bhima (Fluss)
Der Bhima (Marathi: .mw-parser-output .Deva{font-size:120%}@media all and (min-width:800px){.mw-parser-output .Deva{font-size:calc(120% - ((100vw - 800px)/80))}}@media all and (min-width:1000px){.mw-parser-output .Deva{font-size:100%}}भीमा, Kannada: ಭೀಮಾ Telugu: భీమా; manchmal auch Chandrabhaga genannt) ist ein etwa 861 km langer linker Nebenfluss der Krishna; er fließt durch die indischen Bundesstaaten Maharashtra, Karnataka und Telangana.- [en] Bhima River
[es] Río Bhima
El río Bhima (en hindi, भीमा नदी, que significa, el Terrible) es un largo río de la India, el afluente más importante del río Krishna, que vierte sus aguas en el golfo de Bengala. Tiene una longitud de 725 km y drena una cuenca de 48.631 km², similar a países como República Dominicana, Eslovaquía o Bután.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии