geo.wikisort.org - Island
Stolbovoy Island (Russian: Столбовой остров) is a long and narrow island off the southwest side of the New Siberian archipelago in the eastern part of the Laptev Sea. It is located 184 km away from the Siberian coast and 100 km southwest of Kotelny Island, being thus quite detached from the New Siberian island group, although it belongs to the Lyakhov Islands subgroup of the New Siberian Islands.
Stolbovoy
Столбовой остров | |
|---|---|
Island | |
 Satellite image of Stolbovoy Island (Sentinel-2, 2019-08-03). | |
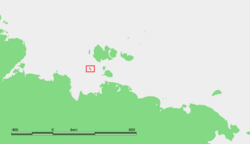 Location of Stolbovoy Island | |
 Stolbovoy | |
| Coordinates: 74°04′15″N 135°59′30″E | |
| Country | Russian Federation |
| Federal subject | Far Eastern Federal District |
| Republic | Sakha Republic |
| Area | |
| • Total | 170 km2 (70 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 222 m (728 ft) |
| Population | |
| • Total | uninhabited |
History
According to Russian tradition in 1690 the Boyar Maxim Mukhoplev visited the island and found a number of crosses, the tombs of Russian seafarers who had previously been there.[1] Stolbovoy was first charted by Yakov Sannikov in 1800.
There was a meteorological station located on the north-west coast of the island at the time of the USSR. In 2012 an automatic GLONASS (Global Navigation Satellite System) monitoring facility was installed in the same spot.[2] Presently the island belongs to the Sakha Republic administrative division of the Russian Federation.
Geography and climate
Stolbovoy Island's area is approximately 170 km². Its length is 47 km and its maximum width is 10 km. The northernmost point of the island was named Cape Toll, in honor of Russian explorer Eduard Toll. There is a 5 km long lake in the northeast of the island. It is separated from the sea by a narrow spit. There is a 13 km long river, the Stolbovoy River, running northwards across the central part of the island.[3]
The highest point of Stolbovoy Island is 222 meters. The island has 15–70 m high rocky cliffs, the lower relief down to the beach being dominated by conical mound-like stony structures.
The climate in the area is exceptionally severe, with prolonged, bitter winters, so that the waters of the Laptev Sea around Stolbovoy Island are covered by ice most of the year.
Geology
Tectonically deformed sedimentary rocks that accumulated during Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous periods comprise Stolbovoy Island. These turbidites, which contain the fossils of marine pelecypods, consist of beds of sandstone coarsely and rhythmically interbedded with beds of siltstone and argillite. These rocks have been folded into a synclinal structure, thrust faulted, and intruded by small quartz diorite dikes.[4][5]
Vegetation
Cryptogam herb covers practically barren Stolbovoy Island. All vegetation consists of dry to wet barren landscapes with scattered, herbs, lichens, mosses, and liverworts. Sedges, dwarf shrubs, and peaty mires are normally absent. These plants form a sparse (2-40%) and low-growing plant cover. The plants often grow in coarse-grained, often calcareous sediments[6]
Views
 |
 |
 |
See also
- Lyakhovsky Islands
- Kigilyakh
- Baydzharakh
References
- Магидович В. И., Магидович И. П. Очерки по истории географических открытий. т. 3. М., 1984. С. 215
- Северный морской путь оснащается современными приборами навигации
- "Река Столбовая". Государственный водный реестр. Retrieved 18 March 2018.
- Kos’ko, M.K., B.G. Lopatin, and V.G. Ganelin, 1990, Major geological features of the islands of the East Siberian and Chukchi Seas and the Northern Coast of Chukotka. Marine Geology. vol. 93, pp. 349–367.
- Fujita, K., and D.B. Cook, 1990, The Arctic continental margin of eastern Siberia, in A. Grantz, L. Johnson, and J. F. Sweeney, eds., pp. 289-304, The Arctic Ocean Region. Geology of North America, vol L, Geological Society of America, Boulder, Colorado.
-
- CAVM Team, 2003, Circumpolar Arctic Vegetation Map. Scale 1:7,500,000. Conservation of Arctic Flora and Fauna (CAFF) Map No. 1. U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, Anchorage, Alaska.
External links
- anonymous, nd, Laptev Sea Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research - Research Unit Potsdam, Potsdam, Germany.
- BirdLife International, 2008, RU118 Stolbovoy island. BirdLife's online World Bird Database: the site for bird conservation. Version 2.1. Cambridge, UK: BirdLife International.
- Grigoriev, M., nda, ice-affected pebble beach of Stolbovoy Island Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research - Research Unit Potsdam, Potsdam, Germany
- Grigoriev, M., ndb, rocky cliffs (15-70 m high) of Stolbovoy Island Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research - Research Unit Potsdam, Potsdam, Germany
На других языках
[de] Stolbowoi
Stolbowoi (russisch Столбовой остров, „Pfeilerinsel“) ist eine etwa 170 km² große, zu den Ljachow-Inseln (Südteil der Neusibirischen Inseln) gehörende, russische Insel in der arktischen Laptewsee.- [en] Stolbovoy Island
[fr] Île Stolbovoï
L'île Stolbovoï (en russe : Столбовой остров) fait partie de l'archipel de Nouvelle-Sibérie situé dans l'océan Arctique, au nord des côtes de la Sibérie orientale entre la mer de Laptev et la mer de Sibérie orientale. Sur le plan administratif elle est rattachée à la République de Sakha (Iakoutie) en Russie.[it] Isola Stolbovoj
L'isola Stolbovoj (in russo Столбовой остров; in italiano "isola Pilastro")[1] fa parte del gruppo delle Ljachov, nell'arcipelago della Nuova Siberia, situato nell'(Oceano Artico).[ru] Столбовой (остров)
Столбовой (якут. Остуолбалаах арыы) — остров в юго-западной части архипелага Новосибирских островов (Республика Саха (Якутия)), в восточной части моря Лаптевых.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии