geo.wikisort.org - Island
San Salvador Island (known as Watling's Island[2] from the 1680s until 1925) is an island and district of The Bahamas. It is widely believed that during Christopher Columbus's first expedition to the New World, this island was the first land he sighted and visited on 12 October 1492. He named it San Salvador after Christ the Saviour.[3][4] Columbus's records indicate that the native Lucayan inhabitants of the territory, who called their island Guanahaní, were "sweet and gentle".[5]
San Salvador Island
Guanahaní Watling's Island | |
|---|---|
Island and District | |
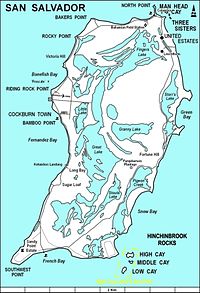 Map of San Salvador Island | |
 San Salvador Island | |
| Coordinates: 24°06′N 74°29′W | |
| Country | |
| Island | San Salvador |
| District | San Salvador |
| Area | |
| • Total | 163 km2 (63 sq mi) |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Total | 930[1] |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern Time Zone) |
| Area code | 242 |

History
When he made landfall on the small island of San Salvador in October 1492, Columbus thought he had reached the East Indies, which was precisely his quest: to find an all-water route to the Orient so that European traders of precious spices could maximise their profits by cutting out Muslim middlemen.[6] Additionally and more specifically, he was working on behalf of the Spanish to surpass the Portuguese, who had established trade routes around the Horn of Africa, a trans-Atlantic route being presumed cheaper and not in danger of Portuguese sabotage that may have been found along the ports around Africa. The island was called Guanahaní by the natives, before its discovery. Columbus described the natives as "sweet and gentle" and also wrote about what the culture of the natives was like. This included wearing minimal clothing and lacking weapons and metals. He also wrote, in his letter to Santangel that "The sierras and the mountains, the plains, the arable and pasture lands, are so lovely and so rich for planting and sowing, for breeding cattle of every kind, for building towns and villages." Thus giving a description of the landscape of the island. In the 17th century, San Salvador was settled by an English buccaneer, John Watling (alternately referred to as George Watling), who gave the island its alternative historical name. The United Kingdom gained control of what are now the Bahamas in the early 18th century. In 1925, the name "San Salvador" was officially transferred from another place, now called Cat Island, and given to "Watling's Island", based on historians believing it to be a more likely match for Columbus's description of Guanahaní. Advocates of Watling's Island included H. Major, the map-custodian of the British Museum; and the geographer Sir Clements Markham,[7] as well as the American sea historian Samuel E. Morison.
The American Fr. Chrysostom Schreiner OSB, the first Catholic priest permanently assigned to the Bahamas, also promoted San Salvador as the correct landing site. In retirement, Fr. Chrysostom relocated to San Salvador, where he was buried. His tomb can still be seen on San Salvador.
From 1957 to 1959 USN Mobile Construction Battalion 7 constructed a LORAN Station on the north end of the island on the shores of Grahams Harbour.[8] The station is now the site of the Gerace Research Centre (formerly known as the Bahamian Field Station).[9] More than 1,000 students and researchers work from the station every year as a base of operations for studying tropical marine geology, biology and archaeology.
Tourism
Today, thanks to its many sandy beaches, the island's main industry is tourism. About 940 people reside on San Salvador Island and its principal community is Cockburn Town, the seat of local government. The town has a population of 271.[10] A Club Med resort, called "Columbus Isle", is located just north of Cockburn Town.
Nearby is the Pleistocene Cockburn Town Fossil Reef.[11] Fossilized staghorn coral (Acropora cervicornis) and elkhorn coral (Acropora palmata) are present near the crest of the fossil reef, and other corals, such as Montastraea annularis, Diploria and Porites, are preserved.
The Gerace Research Centre (formerly the Bahamian Field Station) is located on the north end of the island on the shores of Grahams Harbour.[12] More than 1,000 students and researchers work from the station every year as a base of operations for studying tropical marine geology, biology and archaeology.
The island is home to many shallow-water coral reefs, where snorkellers can observe hundreds of fish species without the use of scuba equipment. It is also known for its quick drop in the submerged platform of the island, allowing for numerous dive sites. The western coast has many wall reefs, with steep drop offs, while the northern coast has many shallow barrier reefs, particularly surrounding Grahams Harbour, a large shallow lagoon.
The island is served by San Salvador International Airport.
The Dixon Hill lighthouse is located on the island south of Dixon Hill Settlement on the east side of the island. It is approximately 160 feet (49 m) tall, and was constructed in 1887 by the Imperial Lighthouse Service.[13] Beside beaches, there are several monuments, ruins and shipwrecks in the area that are major tourist attractions.[14][15]
Hurricanes
Hurricane Lili struck San Salvador in 1996.[16] Hurricane Floyd struck in 1999, and caused damage to homes, tourist facilities, businesses, and infrastructure, and caused considerable beach erosion.[17]
On October 4, 2015, reports from the Bahamas in the wake of Hurricane Joaquin indicated that several islands were, in the words of one journalist, "completely obliterated". Photojournalist Eddy Rafael observed the devastation from the air as part of an assessment flight that included San Salvador Island.[18]
The damage seemed to be confined to just a few specific areas. The Club Med resort on San Salvador was destroyed, Rafael reported, but the power station looked intact from the air. Club Med later stated that much of the landscaping was damaged, but no guests were present at the time of the hurricane and none of the staff were injured.[18]
Physical oceanography
San Salvador Island sits on its own isolated carbonate platform surrounded by a narrow shelf that reaches a depth of up to 40 meters.[19][20] Past the shelf, the slope becomes almost vertical and depth quickly increases to 4,000 meters.[19][21] San Salvador Island experiences a semi-diurnal tide, with two high tides and two low tides per day.[22] Water temperature in San Salvador can range from 23°C to 29°C (73f to 84f) depending on the location and time of year. Salinity and dissolved oxygen are consistent throughout the island and throughout the year (35 ppt and 6.0% respectively).[21]
Most of San Salvador Island is surrounded by fringing reefs.[21] In many areas, such as Fernandez Bay, the shore is rocky and populated by reef urchins (Echinometra viridis). Moving away from shore, the bottom slopes gradually and may have several patch reefs surrounded by a sandy bottom. These patch reefs are home to hundreds of fish, invertebrates, and algae.[21] The depth continues to increase to about 25 meters at the farthest edge of the shelf, which can be between 400 and 1,500 meters from shore.[21]

Antilles Current
Wind and wave action in San Salvador is influenced by the Antilles Current. The Antilles Current originates south of the Bahamas, Puerto Rico, and Cuba and moves northward where it merges with the Gulf Stream.[23][24] This current cools the waters around San Salvador in the summer and warms the water around the island in the winter. This keeps the water temperature relatively mild and consistent throughout the year.[21]
The coasts of San Salvador are very different from each other. The west coast of San Salvador faces the rest of the Bahamas and the Great Bahama Bank. Most of these islands are sheltered from significant winds and wave action. This is also true of San Salvador's west coast; the water is generally calmer and visibility tends to be greater. In contrast, the eastern coast of San Salvador is windward and completely exposed to the rest of the Atlantic Ocean and is not protected by any other geological formations.[20] As a result, wave action is much stronger and visibility is lower. Evidence of currents from the Atlantic Ocean can be found on the east coast in the form of trash and debris on the beaches. During Hurricane Joaquin in October 2015, cargo steamer El Faro went down approximately 50 miles east of San Salvador. Several weeks later, pieces of the containers that had been swept away by the current were reported on the beaches of San Salvador.[25]
Government
The current Administrator is Gilbert C. Kemp.[citation needed]
Gallery
- USCG LORAN Station San Salvador under construction in about 1958
- View of North Point, Rice Bay, and Dixon Hill Settlement, facing north from the lighthouse in 1998.
- View of Grahams Harbour facing west from North Point in 1998. The water tower at left is located at the Gerace Research Centre, but no longer stands.
- Seagrass (Thalassia testudinum) bed with several echinoids (Tripneustes ventricosus), Grahams Harbour
- Elkhorn coral (Acropora palmata) on the crest of Gaulin Reef
References
- "PRELIMINARY POPULATION AND HOUSING COUNT BY ISLAND AND SUPERVISORY DISTRICT, ALL BAHAMAS: CENSUS 2010" (PDF). Bahamas Department of Statistics.
- Stark, James H. (1891). Stark's History and Guide to the Bahama Islands. Boston: Boston Photo Electrotype Co. p. 151. OCLC 1071967476.
- William D. Phillips Jr., "Columbus, Christopher", in David Buisseret (ed.), The Oxford Companion to World Exploration, (Oxford: Oxford University Press, online edition 2012).
- In 1986, the National Geographic Society made an alternative suggestion of Samana Cay. For a brief discussion of the controversy see William D. Phillips, Jr., and Carla Rahn Phillips, The Worlds of Christopher Columbus (Cambridge and New York: Cambridge University Press, 1992), pp. 155-5.
- Brown, Dee. Bury My Heart at Wounded Knee, New York: Henry Holt, p 2.
- Nash, Gary B. Red, White and Black: The Peoples of Early North America Los Angeles 2015. Chapter 1, p. 18
- Herbermann, Charles, ed. (1913). . Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company.
- MCB 7 Cruise book 1957-59, Seabee Museum, Port Hueneme, Ca
- Gerace Research Centre
- SAN SALVADOR POPULATION BY SETTLEMENT AND TOTAL NUMBER OF OCCUPIED DWELLINGS: 2010 CENSUS - Bahamas Department of Statistics
- Curran, HA and B White. Field Guide to the Cockburn Town Fossil Coral Reef, San Salvador, Bahamas. p. 71-96., In Proceedings of the 2nd Symposium on the Geology of The Bahamas, 1984. JW Teeter (ed.).
- Gerace Research Centre
- www.thebahamasguide.com/islands/sansalvador/default.htm "San Salvador" Archived 2012-09-12 at archive.today, The Bahamas Guide, Retrieved 6 March 2001
- http://www.bahamas.com/islands/san-salvador "San Salvador", The Official site of the Bahamas, Retrieved 21 September 2013
- http://www.bahamas.com/islands/san-salvador "San Salvador", The Bahamas, Retrieved 21 September 2013
- Garver, John (January 3, 2003). "Some effects of Hurricane Lili (Oct 1996)". Union College. Retrieved October 10, 2010.
- Curran, H. A., Delano, P., White, B., and Barrett, M., 2001, "Coastal Effects of Hurricane Floyd on San Salvador Island, Bahamas," In Proceedings of the 10th Symposium on the Geology of The Bahamas, 2001. Greenstein, B. J., and Carney, C. K.(eds.)
- "Hurricane Joaquin Exits Bahamas; Several Islands "Completely Obliterated"". The Weather Channel. 3 October 2015. Retrieved 4 October 2015.
- Littler, M.M.; Littler, D.S.; Blair, S.M.; Norris, J.N. (1986). "Deep-water plant communities from an uncharted seamount off San Salvador Island, Bahamas: distribution, abundance, and primary productivity". Deep Sea Research. 33 (7): 881–892. doi:10.1016/0198-0149(86)90003-8.
- Peckol, P.M.; Curran, A.; Greenstein, B.J.; Blair, S.M.; Norris, J.N. (2003). "Assessment of coral reefs off San Salvador Island, Bahamas(stony corals, algae and fish populations)". Atoll Research Bulletin. 496: 124–145. doi:10.5479/si.00775630.496-7.124.
- Gerace, D.T.; Ostrander, G.K.; Smith, G.W. (1998). "San Salvador, Bahamas". Caribbean Coastal Marine Productivity: 229–245.
- "Tide Predictions - San Salvador TEC4631 Tidal Data Daily View - NOAA Tides & Currents". tidesandcurrents.noaa.gov. Retrieved 2017-04-20.
- Talley, L.D. (2011). Descriptive physical oceanography: an introduction. Academic press.
- "Jacksonville Marine Lab/ Bolles School/ Robin Paris drifters deployed in 2016". nefsc.noaa.gov. Retrieved 2017-04-20.
- "Debris piece in Bahamas matches El Faro's cargo log". USA TODAY. Retrieved 2017-04-20.
External links
- High resolution map of the island
- Multi-media exploration of San Salvador's people, plants, sea life, culture and research project topics, Bahamas-Research
- Marine life around San Salvador island, photo gallery
- Herbermann, Charles, ed. (1913). . Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company.
На других языках
[de] San Salvador (Bahamas)
San Salvador ist eine Insel und ein Distrikt am Nordost-Rand der Bahamas. Die Insel hat mit einer Fläche von 94,9 km² eine 11,2 km lange Ost-West- und eine 19,25 km lange Nord-Süd-Ausdehnung. Sie ist mit Ausnahme der Gegend um Cockburn Town im Westen von mehreren Korallenriffen umgeben, sodass für Schiffe nur hier ein Zugang existiert.- [en] San Salvador Island
[es] San Salvador (Bahamas)
San Salvador, conocida también como Isla Watling (inglés: Watling Island), es una de las islas que integran el archipiélago de las Bahamas. Se cree que San Salvador es Guanahani, la isla en la que desembarcó Cristóbal Colón el 12 de octubre de 1492.[fr] San Salvador (Bahamas)
San Salvador est une île de l'archipel des Bahamas, également appelée Colombus Island ou Watling Island.[it] San Salvador (Bahamas)
San Salvador (nota tra il 1680 e il 1925 come isola di Watling) è un'isola delle Bahamas, di cui costituisce anche un distretto; conta 930 abitanti.[1]. Fu la prima terra americana ad essere toccata da Cristoforo Colombo, il 12 ottobre 1492.[ru] Сан-Сальвадор (Багамские острова)
Сан-Сальвадор (англ. San Salvador Island), также известный как Остров Уотлинга, — остров и район Багамских островов. До 1986 года, когда Национальное географическое общество высказало предположение об острове Самана-Ки, бытовало мнение, что во время своей первой экспедиции в Новый свет, остров Сан-Сальвадор был первой землёй, которую увидел и посетил Христофор Колумб 12 октября 1492 года. В документах Колумба сказано, что обитатели территории, на которую он высадился, называли остров — Гуанахани (Guanahani).Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии




