geo.wikisort.org - River
The Madre de Dios River (Spanish pronunciation: [ˈmaðɾe ðe ðjos]) is a river shared by Bolivia and Peru which is homonymous to the Peruvian region it runs through. On Bolivian territory it receives the Beni River, close to the town of Riberalta, which later joins with the Mamore River to become the Madeira River after the confluence. The Madeira is a tributary to the Amazon River.
| Madre de Dios River | |
|---|---|
 Madre de Dios near Boca Manú town, Peru | |
 The Amazon Basin with the Madre de Dios River highlighted | |
| Location | |
| Country | Bolivia, Peru |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • location | Cordillera Vilcanota, Peru |
| Mouth | Madeira River |
• location | Villa Bella, Beni, Bolivia |
| Length | 1,347 km (837 mi) |
| Basin size | 281,000 km2 (108,000 sq mi) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Miraflores-El Sena |
| • average | 5,800 m3/s (200,000 cu ft/s)[1] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Near mouth |
| • average | 9,350 m3/s (330,000 cu ft/s) |
The Madre de Dios is an important waterway for the department of Madre de Dios, particularly Puerto Maldonado, the largest town in the area, and the capital of the department. Mango farming and gold mining are among the many industries on its beaches. Other important industries the Madre de Dios provides are selective logging and farming, both of which are serious environmental problems. Along the length of the river there are several national parks and reserves, notably Tambopata-Candamo National Park, Manú National Park (also known as Manú Biosphere Reserve) and Bahuaja-Sonene National Park.
Hydrography
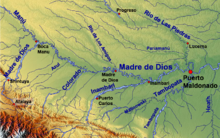
The Madre de Dios serves as the largest watershed in the area, as part of the vast Amazon River watershed. The river's main tributaries include on the right: Chivile, Azul, Blanco, Inambari, Tambopata and Colorado rivers and from the left: Los Amigos, Manú, and Las Piedras.[2]
References
- Molina-Carpio, Jorge; Espinoza, Jhan Carlo; Vauchel, Philippe; Ronchail, Josyane; Gutierrez Caloir, Beatriz; Guyot, Jean-Loup; Noriega, Luis (2017). "Hydroclimatology of the Upper Madeira River basin: Spatio-temporal variability and trends". Hydrological Sciences Journal. 62 (6): 911–927. doi:10.1080/02626667.2016.1267861. S2CID 133578964.
- Evaluacion Ambiental Territorial en la Zona Aurifera de Madre de Dios Archived 2008-12-17 at the Wayback Machine, 4. Climatología E Hidrologia Archived 2008-09-13 at the Wayback Machine {es} Ministry of Energy and Mines, Peruvian Government, December 1997.
External links
- Madre de Dios Watershed at NASA Earth Observatory
- Stroud Water Research Center Project in Madre de Dios, Peru
На других языках
[de] Río Madre de Dios
Der Río Madre de Dios (spanisch für „Muttergottes-Fluss“; Quechua: Amaru Mayu – „Fluss der heiligen Schlange“; Araona: Manutata – „Vater der Flüsse“) ist ein linker Nebenfluss des Río Beni im Südosten Perus und Norden Boliviens.- [en] Madre de Dios River
[es] Río Madre de Dios
El río Madre de Dios pertenece a la cuenca del Amazonas, y que atraviesa los países de Perú y Bolivia. Es afluente del río Beni. Tiene una longitud aproximada de 1 150 km y es un río binacional, ya que discurre por la parte suroriental de Perú (655 km[1] por la departamento de Madre de Dios) y noroccidental de Bolivia. Drena una cuenca de más de 100 000 km².[it] Madre de Dios (fiume)
Il Madre de Dios è un fiume del Perù che reca lo stesso nome della regione che attraversa.[ru] Мадре-де-Дьос (река)
Ма́дре-де-Дьос (Амару-Майо, исп. Río Madre de Dios) — река в Перу и Боливии, в бассейне Амазонки.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии
