geo.wikisort.org - River
The Ontonagon River (/ˌɒntəˈnɑːɡən/ ON-tə-NAH-gən) is a river flowing into Lake Superior at the village of Ontonagon, on the western Upper Peninsula of Michigan in the United States. The main stem of the river is 25 miles (40 km) long[4] and is formed by a confluence of several longer branches, portions of which have been collectively designated as a National Wild and Scenic River.[5] Several waterfalls occur on the river including Agate Falls and Bond Falls.
| Ontonagon River | |
|---|---|
 The Ontonagon River just below the confluence of its east and middle branches, as viewed from near US Highway 45 | |
 | |
| Etymology | Ojibwe Nondon-organ ("hunting river") or Ontonagori ("lost bowl")[1][2] |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Mouth | |
• location | Lake Superior |
• coordinates | 46.87633°N 89.32791°W[3] |
National Wild and Scenic River | |
| Type | Wild, Scenic, Recreational |
| Designated | March 3, 1992 |



Course
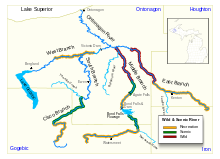
The Ontonagon River's principal tributaries are its West, South, Middle and East branches, all of which flow in part through the Ottawa National Forest:[6]
- The West Branch Ontonagon River[7] is entirely contained in Ontonagon County. It begins at the outlet of Lake Gogebic near the community of Bergland and flows generally east-northeastwardly for approximately 34.5 miles (55.5 km),[8] collecting the South Branch and passing through a dam which forms the Victoria Reservoir.[4][6]
- The South Branch Ontonagon River[9] is formed in southwestern Ontonagon County by the confluence of the short Tenmile Creek and the Cisco Branch Ontonagon River. The Cisco Branch starts in Cisco Lake in eastern Gogebic County and flows generally north-northeastwardly for 32.7 miles (52.7 km)[8] to the South Branch,[10] which then flows northwardly for 33.3 miles (53.6 km),[8] passing the community of Ewen, to join the West Branch.[6]
- The Middle Branch Ontonagon River,[11] 70.7 miles (113.8 km) long,[8] issues from Crooked Lake in eastern Gogebic County and initially flows eastwardly, passing the community of Watersmeet. After collecting the Tamarack River, the Middle Branch turns northwardly into Ontonagon County, where it collects the Baltimore River and joins the East Branch.[6]
- The East Branch Ontonagon River,[12] 59.3 miles (95.4 km) long,[8] issues from Jingle Lake in northern Iron County and flows generally northwestwardly through Houghton County into Ontonagon County, where it joins the Middle Branch.[6]
Below the confluence of its various branches, the Ontonagon River flows generally north-northwestwardly for 24.7 miles (39.7 km)[8] in Ontonagon County to the village of Ontonagon, where it flows into Lake Superior.[6]
National Wild and Scenic River designation
On March 3, 1992, the following reaches of the Ontonagon's upper tributaries were collectively designated the Ontonagon National Wild and Scenic River: The upper courses of the East and Middle branches in the Ottawa National Forest; the Cisco Branch in its entirety; and approximately the middle section of the West Branch, from Cascade Falls to the Victoria Reservoir.[5][6]
Other historical significance
During the mid-19th century, a very large mass of solid, nearly pure copper, the Ontonagon Boulder, was removed from the Ontonagon River. It now is in the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History in Washington, D.C.
See also
- List of Michigan rivers
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ontonagon River. |
- Brothers, Hearne (July 11, 1970). "Michigan State". Hearne Brothers – via Google Books.
- "The Land of Hiawatha: Upper Peninsula of Michigan". Upper Peninsula Development Bureau. July 11, 1928 – via Google Books.
- "Ontonagon River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey.
- The American Rivers Outstanding Rivers List, Second Edition, May 1991. Compiled and edited by Matthew H. Huntington and John D. Echeverria. Washington, DC: American Rivers, Inc.
- "Rivers (U.S. National Park Service)". www.nps.gov.
- Michigan Atlas & Gazetteer (Map). DeLorme. 2003. ISBN 0-89933-335-4.
- U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: West Branch Ontonagon River
- U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline data. The National Map, accessed February 3, 2012
- U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: South Branch Ontonagon River
- U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Cisco Branch Ontonagon River
- U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Middle Branch Ontonagon River
- U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: East Branch Ontonagon River
Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии