geo.wikisort.org - River
The Mahoning River[1] is a river located in northeastern Ohio and a small portion of western Pennsylvania. Flowing primarily through several Ohio counties, it crosses the state line into Pennsylvania before joining with the Shenango River to form the Beaver River. The Mahoning River drops from 1,296 feet (395 m)[1] at the headwaters near Winona to 761 feet (232 m)[1] at the outfall near Mahoningtown, Pennsylvania. It is part of the Ohio River watershed.
| Mahoning River | |
|---|---|
 The Mahoning River in Youngstown, Ohio | |
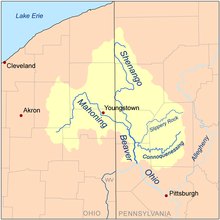 Map of the Beaver River watershed including the Mahoning River | |
| Location | |
| Country | United States |
| States | Ohio, Pennsylvania |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • location | One half mile southwest of Winona, Ohio |
| • coordinates | 40°49′18″N 80°54′12″W[1] |
| • elevation | 395 m (1,296 ft) above sea level[2] |
| Mouth | Beaver River |
• location | near Mahoningtown, New Castle, Pennsylvania |
• coordinates | 40°57′29″N 80°22′43″W[1] |
• elevation | 232 m (761 ft) above sea level[1] |
| Length | 182 km (113 mi)[3] |
| Basin size | 2,932 km2 (1,132 sq mi) |
| Discharge | |
| • average | 54 m3/s (1,900 cu ft/s)[3] |
Tributaries
North Shore
- Marshall Run
- Grays Run
- Dry Run
- Little Squaw Creek
- Mosquito Creek
- Chocolate Run
- Eagle Creek
- West Branch
- Kale Creek
- Willow Creek
- Deer Creek
- Beech Creek
- Beaver Run
South Shore
- Hickory Run
- Hines Run
- Yellow Creek
- Mill Creek (Austintown)
- Fourmile Run
- Meander Creek
- Mud Creek
- Duck Creek
- Lawson Run
- Charley Run Creek
- Mill Creek (Berlin)
- Island Creek
- Fish Creek
Hydronymy
The name comes from Lenape mahonink, meaning "at the licks" or "there is a lick", referring to historic salt licks in the area.[4][5]
Physical properties
This section does not cite any sources. (July 2012) |


The river is formed near Winona in Columbiana County, Ohio, and extends for a length of approximately 113 miles (182 km), with a watershed area of approximately 1,132 square miles (2,932 km²). It joins the Shenango River near Mahoningtown, Pennsylvania south of New Castle to form the Beaver River. The river traverses five Ohio counties,[1] Columbiana, Stark, Portage, Trumbull, and Mahoning, as well as Lawrence County, Pennsylvania. The watershed area also includes parts of Ashtabula and Geauga counties in Ohio.
The three main tributaries are Mosquito Creek, West Branch, and Eagle Creek, all in Ohio. There are 15 dams on the river course. The river has a course of 97.1 miles (156.3 km) in Ohio, with the remainder in Pennsylvania.
The river supports more than 72 species of fish and 15 species of freshwater mussels.
The river is roughly divided into two sections based on its own character and its surroundings. In addition to the change in terrain address in the section on "Floods", the level of human development changes dramatically as well. The “upper elevation” flowing north and east extends roughly from Winona to Leavittsburg and is generally rural in nature, meandering through game lands, forests, and agricultural properties. The mainstem (lower elevation) flowing mainly southeast extends roughly from Leavittsburg to the river's mouth near New Castle, Pennsylvania. Portions of this section are more densely populated and heavily industrialized, including the cities of Warren, Niles, Youngstown, Campbell, and others. The area suffers with residue from all the industrial activity that began in the late 19th century. The mainstem area has a population of over 500,000 and has a long history of steel making, coke production, and other industries.
Environmental concerns
This section does not cite any sources. (December 2015) |
The industrial nature of the mainstem area has caused considerable pollution in the river. Much of the pollution has left the ecosystem via the natural river flow. But analysts estimate that 750,000 cubic yards (573,416 m³) of river bed and shoreline sediment, over a 30-mile (48.2 km) stretch of the mainstem from Leavittsburg to the Pennsylvania border, is so heavily polluted that it will need to be remediated. Approximately 45% of this material is located in the vicinity of the Girard Dam near Girard, Ohio, which has acted as a trap for much of the contaminated sediment.
Petroleum hydrocarbons, benzo(a)pyrene (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons), and mercury have all been found in quantities several times the maximum safe levels. Since 1988, the Ohio Department of Health has maintained an advisory against swimming or wading in the river between Leavittsburg and the Pennsylvania border, and also advises against eating fish caught there. The Corps of Engineers estimates that the remediation will take up to 15 years to complete and cost in excess of US$100 million.
Cities and towns along its course include:
- Winona, Ohio
- Alliance, Ohio
- Sebring, Ohio
- Newton Falls, Ohio
- Leavittsburg, Ohio
- Warren, Ohio
- Niles, Ohio
- McDonald, Ohio
- Girard, Ohio
- Youngstown, Ohio
- Campbell, Ohio
- Struthers, Ohio
- Lowellville, Ohio
- Edinburg, Pennsylvania
- Mahoningtown, Pennsylvania
Floods
The Mahoning river is susceptible to frequent flooding during high rain events. A days long flood lasted almost continuously from March 23 to March 26, 1913. Youngstown residents were without water. Damage reached to communities throughout the area, such as Leavittsburg and Lowellville. Losses to the busy industrial area in the region reached the millions of dollars. Flood waters nearly reached the roofs of Republic Steel's plant. Some damaged bridges collapsed. Several water control infrastructure projects followed: The Lake Milton dam was built from 1913 to 1917.[6]
Another dramatic flooding event started when three days of torrential rain fell in July 2003,[7] resulting in such high volume that the river changed its course in Leavittsburg, flooding and destroying nearly 100 homes. For much of the upper half of the river, the land is relatively flat with minimal relief to confine the river. This makes it prone to change courses during high-water events. Around Youngstown, the river valley becomes much more pronounced and the river is more constrained, although there is still room for localized avulsions.
See also
- List of rivers of Ohio
- List of rivers of Pennsylvania
- Mahoning Valley
References
- U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Mahoning River
- Hanoverton, OH, 7.5 Minute Topographic Quadrangle, USGS, 1994 (1997 rev.)
- "mahoningriver,com". Archived from the original on 2006-08-21. Retrieved 2006-03-15.
- "Ohio County Name Origins" (PDF). Ohio Secretary of State. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 July 2013. Retrieved 25 February 2019.
- Gannett, Henry (1905). The Origin of Certain Place Names in the United States. U.S. Government Printing Office. p. 196.
- Mahoning Valley Historical Society, "The Flood of 1913," March 14, 2013 https://mahoninghistory.org/2013/03/14/the-great-flood-of-1913/
- "Mahoning River Watershed Action Plan" (PDF). Youngstown State University. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-14. Retrieved 2011-03-01.
External links
- Archived version of Youngstown State University's Mahoning River Watershed website
- Archived version of Mahoning River Consortium website
На других языках
[de] Mahoning River
Der Mahoning River ist ein 182 km langer Fluss im nordöstlichen US-Bundesstaat Ohio und im westlichen Pennsylvania. Er bildet im Zusammenfluss mit dem Shenango River den Beaver River. Der Abfluss erfolgt über den Ohio River und den Mississippi River in den Golf von Mexiko. Der Mahoning River gehört zum Flusssystem des Mississippi und entwässert ein Gebiet von 2.932 km2. Die Quelle befindet sich bei der Ortschaft Winona im Columbiana County, Ohio. Der Mahoning River fließt zunächst in nordöstlicher Richtung, biegt nach rund 70 km bei Leavittsburg im rechten Winkel nach Südosten ab und vereinigt sich bei New Castle, Pennsylvania, mit dem Shenango River.[2]- [en] Mahoning River
[ru] Махонинг
Махонинг (англ. Mahoning River) — река на востоке штата Огайо и на западе штата Пенсильвания, США. Длина составляет 182 км, из них 156,3 км — в штате Огайо; площадь бассейна — около 2932 км². Средний расход воды — 54 м³/с. Вблизи города Ньюкасл, штат Пенсильвания, Махонинг сливается с рекой Шенанго и образует реку Бивер, которая является притоком реки Огайо. Река протекает по территории пяти округов штата Огайо: Колумбиана, Старк, Портидж, Трамбулл и Махонинг, а также по территории округа Лоренс штата Пенсильвания. Крупнейшие притоки: Москито-Крик, Уэст-Бранч, Игл-Крик, Милл-Крик и Йеллоу-Крик[1]. На реке построено 15 плотин.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии